Element Magnesium - Mg
Comprehensive data on the chemical element Magnesium is provided on this page; including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides of Magnesium. Common chemical compounds are also provided for many elements. In addition technical terms are linked to their definitions and the menu contains links to related articles that are a great aid in one's studies.
Magnesium Menu
- Magnesium Page One
- Magnesium Page Two
- Magnesium Page Three
Overview of Magnesium

Mg Electrons Gained Or Lost
- Mg + Cl 2- Mg 2+ + 2Cl-Magnesium loses electrons and is therefore said to be 'oxidized', whereas the chlorines gain electrons and are said to be reduced. Another way to judge that the chlorine has been reduced is the fact that the charge on the atoms is made more negative, or reduced.
- MG Electronics is a leading manufacturer of products utilized by OEM, Distributors and professional equipment installers thoughout North America.
Magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH) 2 Magnesium nitrate Mg(NO 3) 2 Magnesium oxide (MgO) Magnesium peroxide (MgO 2) Magnesium sulfate (MgSO 4) Interesting facts: It is the eighth most common element in the earth's crust, but is the most commercially used element. It is obtained from seawater. It is a very flammable metal. The center of chlorophyll.
- Atomic Number: 12
- Group: 2
- Period: 3
- Series: Alkali Earth Metals
Magnesium's Name in Other Languages
- Latin: Magnesium
- Czech: Hořčík
- Croatian: Magnezij
- French: Magnésium
- German: Magnesium - r
- Italian: Magnesio
- Norwegian: Magnesium
- Portuguese: Magnésio
- Russian: Магний
- Spanish: Magnesio
- Swedish: Magnesium
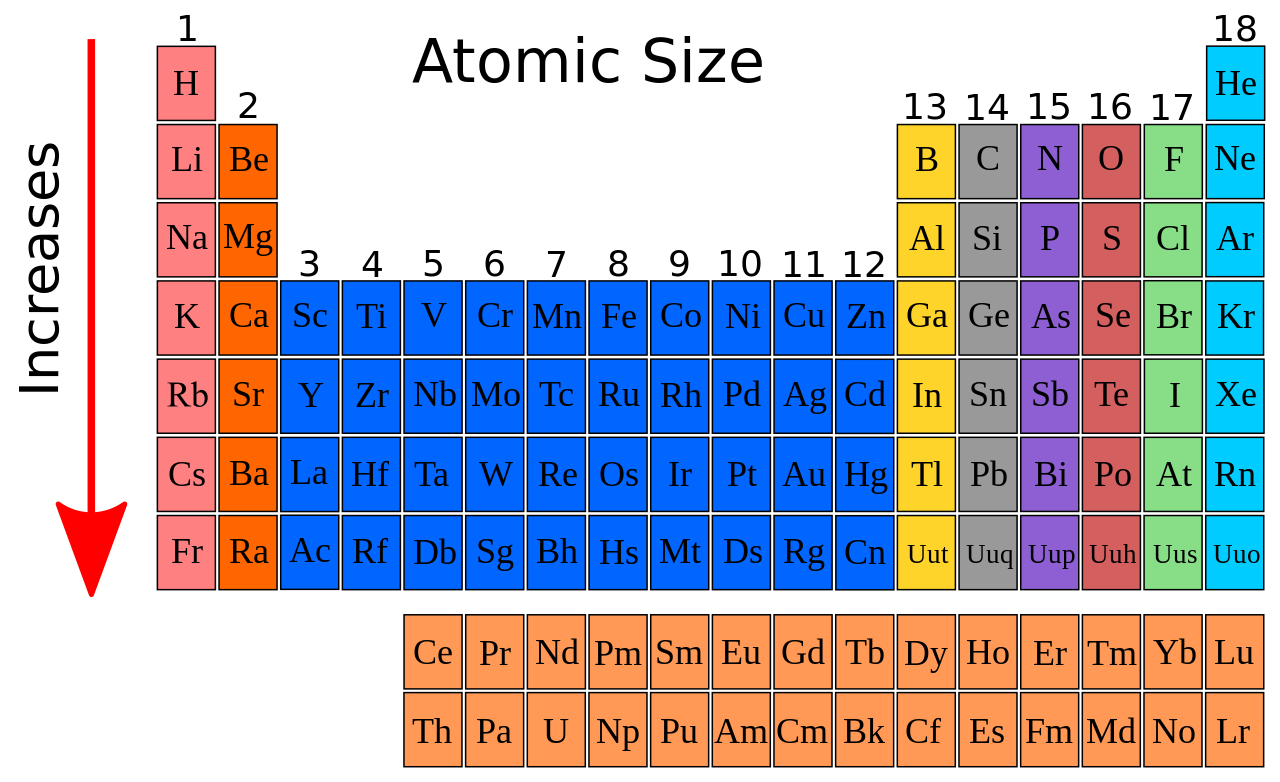
Atomic Structure of Magnesium
- Atomic Radius: 1.72Å
- Atomic Volume: 13.97cm3/mol
- Covalent Radius: 1.36Å
- Cross Section (Thermal Neutron Capture)σa/barns: 0.063
- Crystal Structure: Hexagonal
- Electron Configuration:
- 1s2 2s2p6 3s2
- Electrons per Energy Level: 2,8,2
- Shell Model
- Shell Model
- Ionic Radius: 0.72Å
- Filling Orbital: 3s2
- Number of Electrons (with no charge): 12
- Number of Neutrons (most common/stable nuclide): 12
- Number of Protons: 12
- Oxidation States: 2
- Valence Electrons: 3s2
- Electron Dot Model
- Electron Dot Model
Chemical Properties of Magnesium
- Electrochemical Equivalent: 0.45341g/amp-hr
- Electron Work Function: 3.66eV
- Electronegativity: 1.31 (Pauling); 1.23 (Allrod Rochow)
- Heat of Fusion: 8.954kJ/mol
- Incompatibilities:
- Ionization Potential
- First: 7.646
- Second: 15.035
- Third: 80.143
- Valence Electron Potential (-eV): 40
Physical Properties of Magnesium
- Atomic Mass Average: 24.305
- Boiling Point: 1363K 1090°C 1994°F
- Coefficient of lineal thermal expansion/K-1: 26.1E-6
- Conductivity
- Electrical: 0.226 106/cm Ω
Thermal: 1.56 W/cmK
- Electrical: 0.226 106/cm Ω
- Density: 1.738g/cc @ 300K
- Description:
- Grayish-white metal. Reacts with hot water and burns in air when ignited.
- Elastic Modulus:
- Bulk: 35.6/GPa
- Rigidity: 17.3/GPa
- Youngs: 44.7/GPa
- Enthalpy of Atomization: 148.5 kJ/mole @ 25°C
- Enthalpy of Fusion: 8.95 kJ/mole
- Enthalpy of Vaporization: 128.7 kJ/mole
- Flammablity Class:
- Freezing Point:see melting point
- Hardness Scale
- Brinell: 260 MN m-2
- Mohs: 2.5
- Heat of Vaporization: 127.4kJ/mol
- Melting Point: 922K 649°C 1200°F
- Molar Volume: 13.97 cm3/mole
- Optical Reflectivity: 74%
- Physical State (at 20°C & 1atm): Solid
- Specific Heat: 1.02J/gK
- Vapor Pressure = 361Pa@649°C
Regulatory / Health
- CAS Number
- 7439-95-4
- OSHAPermissible Exposure Limit (PEL)
- No limits set by OSHA
- OSHA PEL Vacated 1989
- No limits set by OSHA
- NIOSHRecommended Exposure Limit (REL)
- No limits set by NIOSH
- Levels In Humans:
Note: this data represents naturally occuring levels of elements in the typical human, it DOES NOT represent recommended daily allowances.- Blood/mg dm-3: 37.8
- Bone/p.p.m: 700-1800
- Liver/p.p.m: 590
- Muscle/p.p.m: 900
- Daily Dietary Intake: 250-380 mg
- Total Mass In Avg. 70kg human: 19 g
- Discovery Year: 1808
- Name Origin:
- Greek: From Magnesia a district of Thessaly.
- Abundance of Magnesium:
- Earth's Crust/p.p.m.: 23000
- Seawater/p.p.m.: 1200
- Atmosphere/p.p.m.: N/A
- Sun (Relative to H=1E12): 4E+07
- Sources of Magnesium:
- Usually obtained by electrolysis of melted magnesium chloride (MgCl2) found in sea water. World production is around 350,000 tons per year. Primary mining areas are Austria, China, Poland, Russia, USA, India, Greece and Canada.
- Uses of Magnesium:
- Used in alloys to make airplanes, missiles, racing bikes and other things that need light metals. Also used in fireplace bricks, flashbulbs, pigments and filters.
- Additional Notes:
- In 1755 Joseph Black in Edinburgh Scotland recognized magnesium as an element, however, it wasn't issolated until 1808 by Sir Humphrey Davy.
Magnesium Menu
- Magnesium Page One
- Magnesium Page Two
- Magnesium Page Three

References
A list of reference sources used to compile the data provided on our periodic table of elements can be found on the main periodic table page.
Related Resources
- Anatomy of the Atom
Answers many questions regarding the structure of atoms. - Molarity, Molality and Normality
Introduces stoichiometry and explains the differences between molarity, molality and normality. - Molar Mass Calculations and Javascript Calculator
Molar mass calculations are explained and there is a JavaScript calculator to aid calculations. - Chemical Database
This database focuses on the most common chemical compounds used in the home and industry.
Citing this page
If you need to cite this page, you can copy this text:
Kenneth Barbalace. Periodic Table of Elements - Magnesium - Mg. EnvironmentalChemistry.com. 1995 - 2021. Accessed on-line: 4/25/2021
https://EnvironmentalChemistry.com/yogi/periodic/Mg.html
.
Mg Unpaired Electrons
Linking to this page
Mg Electrons And Protons
If you would like to link to this page from your website, blog, etc., copy and paste this link code (in red) and modify it to suit your needs:
<a href='https://EnvironmentalChemistry.com/yogi/periodic/Mg.html'>echo Periodic Table of Elements: Magnesium - Mg (EnvironmentalChemistry.com)</a>- Comprehensive information for the element Magnesium - Mg is provided by this page including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides and technical terms are linked to their definitions.
.
NOTICE: While linking to articles is encouraged, OUR ARTICLES MAY NOT BE COPIED TO OR REPUBLISHED ON ANOTHER WEBSITE UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES.
Electrons Mg Plus 2
PLEASE, if you like an article we published simply link to it on our website do not republish it.
